命题逻辑
命题逻辑(Propositional Logic)
Propositional = an expression(表达) in language or signs(标志) of something that can be believed(相信), doubted(质疑), or denied(否认) or is either true or false(真或假)
命题符号
在逻辑学中,P、Q 和 R 通常代表命题或布尔变量,它们可以用来构造复杂的逻辑表达式。
逻辑链接
逻辑与
合取(AND): P ∧ Q
逻辑或
析取(OR): P ∨ Q
如果要求P和Q不能同时为真,R = ¬(P↔Q)
逻辑非
否定(NOT): ¬P
逻辑条件
条件(IMPLY): P → Q
当条件P为False时,P不影响Q,所以两种情况都是成立的
P |
Q |
P → Q |
|---|---|---|
| T | T | T |
| T | F | F |
| F | T | T |
| F | F | T |
逻辑双条件
双条件(BICONDITIONAL): P ↔ Q`
P ↔ Q 等价于 (P → Q) ∧ (Q → P)
P |
Q |
P ↔ Q |
|---|---|---|
| T | T | T |
| T | F | F |
| F | T | F |
| F | F | T |
模型检测算法
模型(model): 给一个命题符号赋予真假值
P: It is raining Q: it is a Tuesday
{P = true, Q = false}
蕴含
蕴含(Entailment): $ A \models B $
在每个model中,如果A是真的,那么B也是真的
推理
推理(Inference), 从已有的命题(sentences),推出新的命题的过程
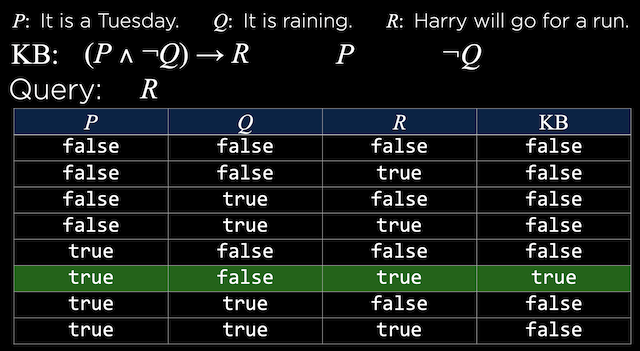
P: It is raining
Q: it is a Tuesday
R: Harray will go for a run.
(知识库)KB:
$ (P \land \neg Q) \rightarrow R $
$ P $
$ \neg Q $
推理(Inference):
$ R $
为了判断: $ KB \models \alpha $
- 枚举所有可能的model
- 如果在每一个model中KB是真值,$\alpha$也是真值。那么$KB \models \alpha$
- 否则,无法推断出来
代码
代码将所有的的symbols真假排列组合成models, 验证每一个model, 如果KB能够验证通过, 给出相应的查询结果
def model_check(knowledge, query):
"""Checks if knowledge base entails query."""
def check_all(knowledge, query, symbols, model):
"""Checks if knowledge base entails query, given a particular model."""
# If model has an assignment for each symbol
if not symbols:
# If knowledge base is true in model, then query must also be true
if knowledge.evaluate(model):
return query.evaluate(model)
return True
else:
# Choose one of the remaining unused symbols
remaining = symbols.copy()
p = remaining.pop()
# Create a model where the symbol is true
model_true = model.copy()
model_true[p] = True
# Create a model where the symbol is false
model_false = model.copy()
model_false[p] = False
# Ensure entailment holds in both models
return (check_all(knowledge, query, remaining, model_true) and
check_all(knowledge, query, remaining, model_false))
# Get all symbols in both knowledge and query
symbols = set.union(knowledge.symbols(), query.symbols())
# Check that knowledge entails query
return check_all(knowledge, query, symbols, dict())
解析推理
推理规则
\[\begin{align} (\alpha \rightarrow \beta) \land \alpha \models \alpha \\ (\alpha \land \beta) \models \alpha \\ \neg(\neg\alpha) \models \alpha \\ \alpha \rightarrow \beta \models \neg\alpha \lor \beta \\ \alpha \leftrightarrow \beta \models (\alpha \rightarrow \alpha) \land (\beta \rightarrow \alpha) \\ \neg(\alpha \land \beta) \models \neg\alpha\lor\neg\beta \\ \neg(\alpha \lor \beta) \models \neg\alpha\land\neg\beta \\ (\alpha\land(\beta\lor\gamma)) \models (\alpha\land\beta)\lor(\alpha\land\gamma) \\ (\alpha\lor(\beta\land\gamma)) \models (\alpha\lor\beta)\land(\alpha\lor\gamma) \\ \end{align}\]合取范式
合取范式(conjunctive normal form), 可以使用上溯推理规则转化成合取范式CNF
\[\begin{align} CNF = (C_1 \land C_2 \land \cdots \land C_n) \\ C_i = (L_1 \lor L_2 \lor \cdots \lor L_m) \end{align}\]为了判断: $ KB \models \alpha $, 采用反证法,将其展开为CNF
- 判断是否: $ KB \land \neg\alpha 是矛盾的$
- 如果矛盾,则 $ KB \models \alpha $
- 否则,无法推断出来
一阶逻辑
Gilderoy, Minerva, Pomona, and Horace each belong to a different one of the four houses: Gryffindor, Hufflepuff, Ravenclaw, and Slytherin.
- Gilderoy belongs to Gryffindor or Ravenclaw.
- Pomona does not belong to Slytherin.
- Minerva belongs to Gryffindor.
如果使用命题逻辑将有16个命题变量
| Gryffindor | Hufflepuff | Ravenclaw | Slytherin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gilderoy | GilderoyGryffindor | GilderoyHufflepuff | GilderoyRavenclaw | GilderoySlytherin |
| Minerva | MinervaGryffindor | MinervaHufflepuff | MinervaRavenclaw | MinervaSlytherin |
| Pomona | PomonaGryffindor | PomonaHufflepuff | PomonaRavenclaw | PomonaSlytherin |
| Horace | HoraceGryffindor | HoraceHufflepuff | HoraceRavenclaw | HoraceSlytherin |
变量
| Constant Symbol | Predicate Symbol |
|---|---|
| Minerva | Person |
| Pomona | House |
| Horace | BelongsTo |
| Gilderoy | |
| Gryffindor | |
| Hufflepuff | |
| Ravenclaw | |
| Slytherin |
公式
复合方程(Compound Formulas) = 通过逻辑联结词(如 ∧, ∨, →, ¬)将原子公式(atomic formulas)组合起来
Person(Minerva) #Minerva is a person.
House(Gryffindor) #Gryffindor is a house.
¬House(Minerva) #Minerva is not a house.
BelongsTo(Minerva, Gryffindor) #Minerva belongs to Gryffindor.
量化公式(Quantified Formulas)= 全称量化公式(Universal Quantified Formula)+ 存在量化公式(Existential Quantified Formula)两种
# ∀x = for Any/All x, ∃x = Exist a x
∀x. BelongsTo(x, Gryffindor) → ¬BelongsTo(x, Hufflepuff) #对于任意x, 他在Gryffindor就不能在Hufflepuff中
∃x. House(x) ∧ BelongsTo(Minerva, x) #存在一个学院x, 学生Minerva属于x
∀x. Person(x) → (∃y. House(y) ∧ BelongsTo(x, y)) #任意一个学生x,存在学院y,x属于y
还有二阶逻辑,三阶逻辑等, 为了表示更复杂的逻辑
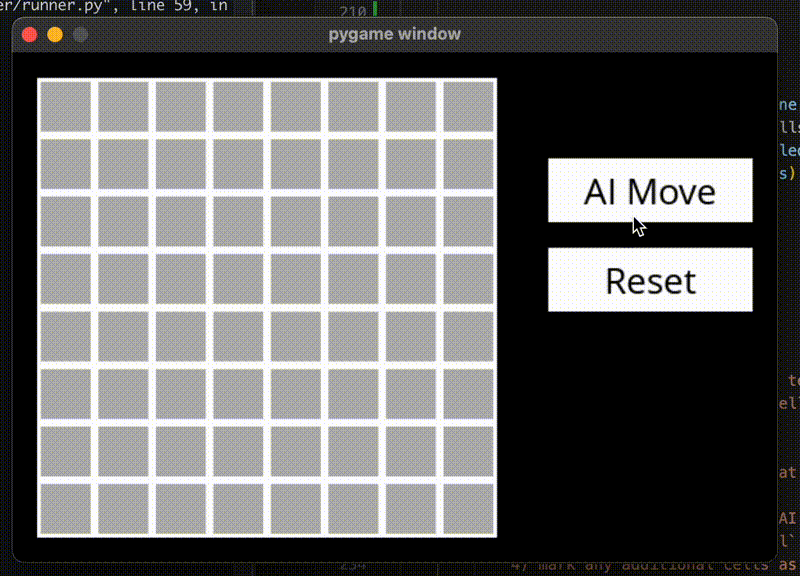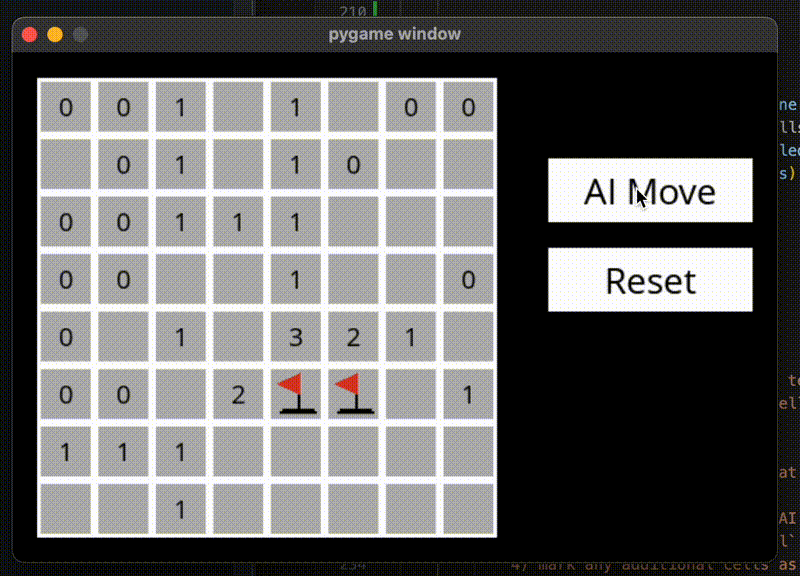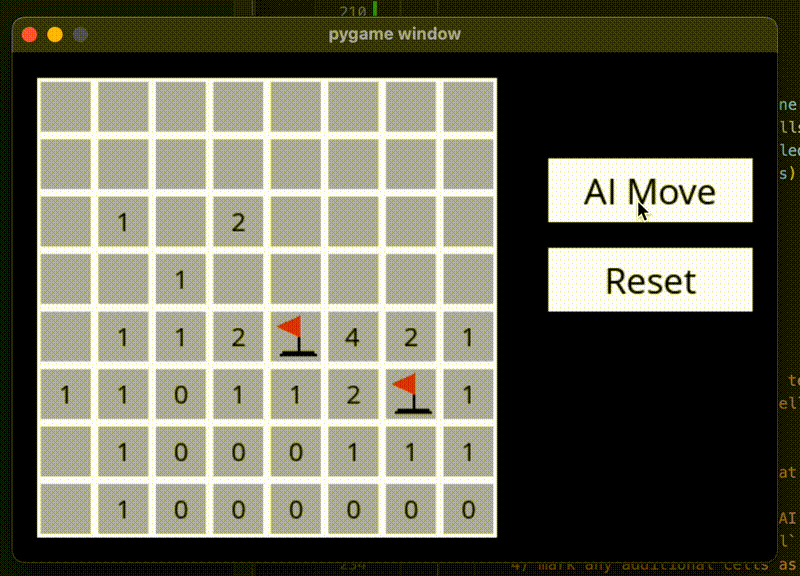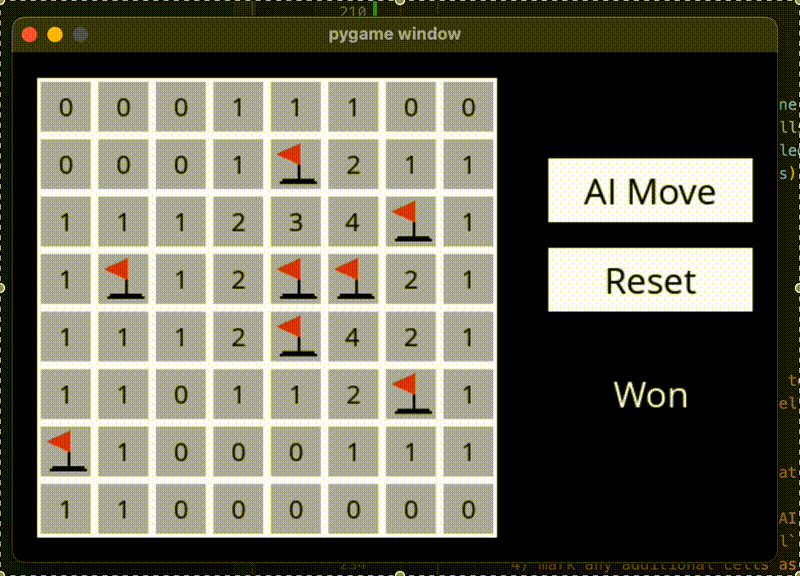
扫雷
知识表示
扫雷游戏,一个数字会显示上下左右斜8个位置, 知识表示如下
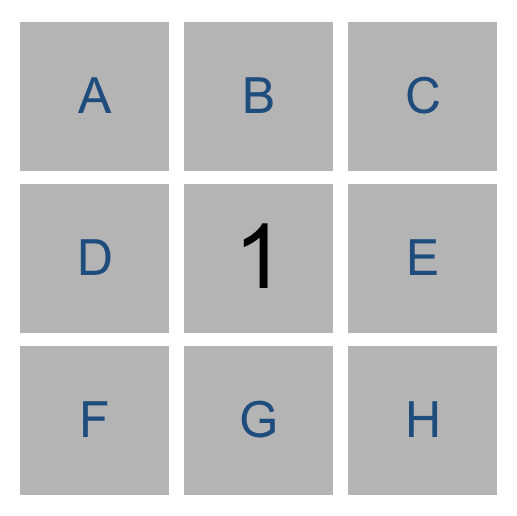
{A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H} = 1
# 1. 如果左边个数 == 右边个数, 那么所有节点雷
# 2. 如果右边个数 == 0, 那么所有节点都安全
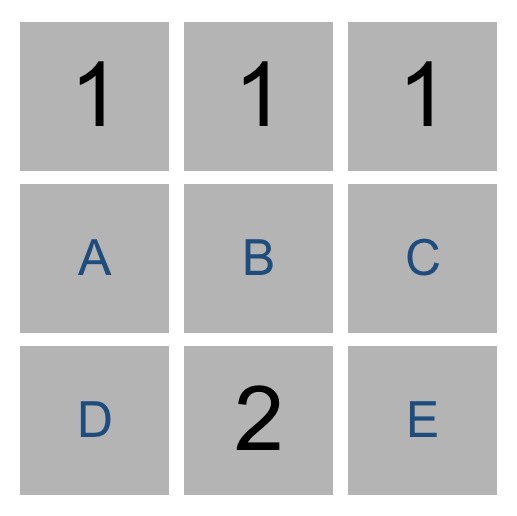
{A, B, C} = 1
{A, B, C, D, E} = 2
# 则有:
{D, E} = 1
运行结果
在无法确定安全区域的时候,使用随机猜测,可能就失败了
– END –